


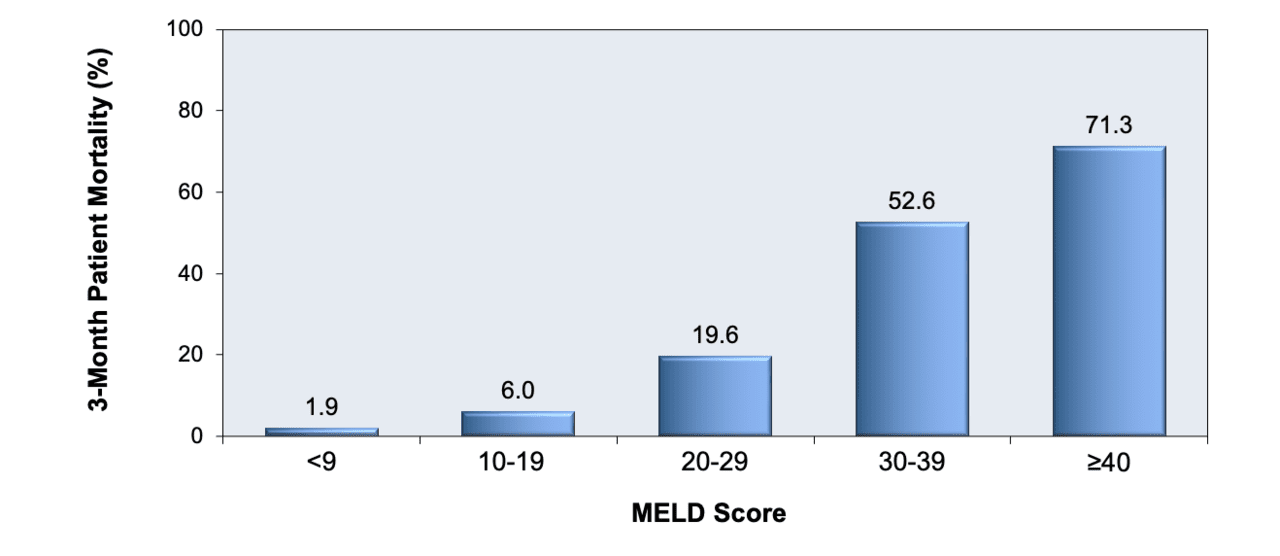
MELD is superior to MELD-Na for predicting 30-day and, perhaps, 90-day mortality after TIPS placement. MELD and MELD-Na both accurately predicted the length of hospital stay after TIPS placement ( p = 0.005 and p = 0.01, respectively). This calculator is recommended for ages 12 and older. Calculating Your MELD Score A MELD score is calculated using the results of key laboratory tests, as well as any recent dialysis data related to renal (kidney) failure. In the sample MELD calculator below, the current calculator tab view. When the maximal inflection point for MELD and MELD-Na was analyzed on the basis of 90-day mortality, a score of 23 was found to be most significant for both MELD (OR, 6.6 95% CI, 1.5-29.1 p = 0.01) and MELD-Na (OR, 3.3 95% CI, 1.1-9.6 p = 0.03). In 2016, serum sodium was added to the MELD score formula, with other changes currently being evaluated. The Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score was developed in 2000 to predict mortality in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation. In a comparison of the ROC AUCs for MELD and MELD-Na, MELD showed improved prediction of 30-day mortality ( p = 0.06) but did not significantly vary in prediction of 90- and 365-day mortality ( p = 0.80 and p = 0.76, respectively). The primary outcomes were death within 30 days and 90 days after TIPS placement (30- and 90-day mortality, respectively), and secondary outcomes included death within 365 days after TIPS placement (365-day mortality), length of hospital stay, and readmission to the hospital within 30 days of TIPS placement. Determines 10-year risk of heart disease or stroke. Two hundred and nineteen consecutive patients who underwent TIPS placement were retrospectively reviewed. ASCVD (Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease) 2013 Risk Calculator from AHA/ACC. The purpose of this study was to compare the ability of the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and sodium MELD (MELD-Na) scoring systems to predict outcomes after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
